cabon 13 nmr spectroscopy pdf
wood word fieser rule
CONTENT
:-
v Object
v introduction
v wood word
fieser Rule
v wood word
fieser rule for conjugated dienen
v homoannular
diene
v hetroannular
dinen
v exocyclica
and endocyclic double bond
v extra
conjugation
v Conjugated dienen correaltions
v implementaion
v base value
of α,β unsturated compounds
v Reference
OBJECTIVE
:-
To familiraze the woodword fieser rule . To calculate
the maximum wavelength of organic
compound
INTRODUCTION :-
Woodward's rules, named after Robert Burns
Woodward and also known as Woodward–Fieser rules (for Louis
Fieser) are several sets of empirically derived rules which attempt to predict
the wavelength of the absorption maximum (λmax) in
an ultraviolet–visible spectrum of a given compound. Examples
are conjugated carbonyl compounds, conjugated dienes, and polyenes.
Robert burn wood word luis fedrick fieser
WOOD WORD
FIESER RULE :-
According to the wood ward fischer rule the λmax of the
molecule can be calculated by using a formula :-
λmax = Base value + ∑substituents- contributes + ∑
other contributes
Base value :- Each type of diene or triene system is having a
certain fixed value at which absorption take place, this value is known as base
value.
In this Rule we will discuss 3 important point in which compound and their base value
1. wood word
fieser rule for conjugated dienes correlation
2. parent
value and incresment for different substituents
3. Wood word
fieser rule for α,β unsaturatd carbonyl
compound or ketons
WOOD
WORD FIESER RULE FOR CONJUGATED DIENES:-
The following are types of conjugated dienes
1.
Homoannuler diene :-
in this type of dienes both double bond contained in one
ring.
And the base value of homoannular diene = 253 nm
2. Hetroannular diene :-
in this type of diene both double bond distributed between two rings.
base value of hetroannular diene system are 214 nm.
3. Endo
cyclic double bond :– double bond present in a ring.
4.
Exocyclic double bond :- double bond in which one of the
double bond atom is a part of a ring.
5. Double
bond extending :– when more double bond are present other than conjugated.
Different
base value :-
Acyclic conjugated diene or Hetero annular conjugated
diene has 215 nm wavelength.
Homo annular conjugated diene :-253 nm
Acyclic trienes :- 245nm
Implemention
:-
|
Conjugated dienes correlation |
Standard (nm) |
|
|
(A). parent value |
|
|
|
Base value for heteroannular diene |
214nm |
|
|
Base value for homo annular diene |
253nm |
|
|
Buta diene system or cyclic conj. Diene |
217nm |
|
|
Acyclic trienes |
245nm |
|
|
(B). incresment for each substituents |
|
|
|
Alkyl substituent or ring residue |
5nm |
|
|
Exocyclic double bond |
5nm |
|
|
Extending conjugation |
30nm |
|
|
(c). Auxochrome |
|
|
|
-OCOCH3 |
0nm |
|
|
-Cl , -Br |
5nm |
|
|
-OR |
6nm |
|
|
-SR |
30nm |
|
|
-NR3 |
60nm |
|
|
Base value |
Standard (nm) |
|
Ar COR |
246nm |
|
ArCHO |
250nm |
|
ArCO2H |
230nm |
|
Incresments |
|
|
Alkyl groups or ring residue O,M-position |
3nm |
|
Alkyl groups or ring residue at P- position |
10nm |
|
Auxochromes |
Ortho Position(nm) |
Meta Position(nm) |
Para Position(nm) |
||
|
-OH |
7 |
7 |
25 |
||
|
-OCH3 |
7 |
7 |
25 |
||
|
-O |
11 |
20 |
78 |
||
|
-Cl |
0 |
0 |
10 |
||
|
-Br |
2 |
2 |
15 |
||
|
-NH2 |
13 |
13 |
58 |
||
|
-NHCOCH3 |
20 |
20 |
45 |
||
|
-N(CH3)2 |
20 |
20 |
85 |
||
Example of Conjugated
diene correlations :-
example 2 :-
example 3:-
example 4:-
Wood word fiser rule
for unsaturated compound:-
in this type of compound carbonyl
group are attached alfa-beta position of double bond
these compound are many following
types –
1. α,β
unsaturatd acid :-
these compound have –COOH group are
attached double bond from α,β position.
Base value of α,β unsaturatd acid:- 195nm.
2. α,β
unsaturatd aldehyde :-
these compound have –CHO group are
attched double bond from α,β position.
Base value of these compound :-
207nm
3. α,β unsaturatd ketone:-
these compound are two type
if compound are persant in cyclic form then base
value of these type compound are 215nm
and if compound are persant in acyclic
form then compound value are 214nm
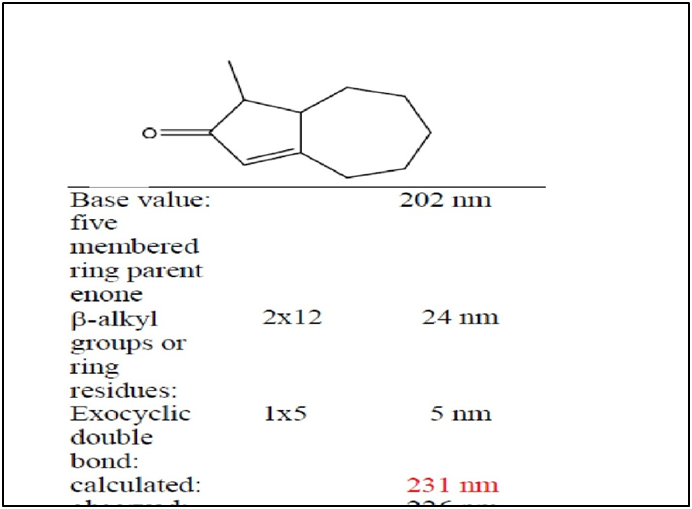
NOTE :-
if cyclic keton are persant in 5
membed ring then base value are 202nm
References :-
1. wood word,
robert burns 1941”strcture and the
absorption spectra of α,β unsaturatd
ketones”
2. Louis
f.fieser, mary fieser (1948) “absorption
spectroscopy and strcture of the diosterols
3. William
reusch – “UV visible spectroscopy”
4. Neil glaovich – (2007-19) “ wood word fieser rule for dienes “
THANK YOU
bharat ke uttari maidan
भारत का भौतिक स्वरूप
भूआकृतिक दृष्टि से भारत को चार भागों में बाँटा जाता है1. उत्तरी पर्वतीय भूभाग :
- यह मूलतः यूरेशिया प्लेट का एक खंड है।
- इसका निर्माण हिमालय से पहले हो चुका था।
- भारत की सबसे ऊँची चोटी K2या गाडबिन आस्टिन (8611 मी.) है जो काराकोरम की सर्वोच्च चोटी है।
- यह अवसादी चट्टानों का बना है।
- इसकी औसत ऊँचाई 6100 मी.. 2500 किमी. और चौड़ाई 25 किमी. यह पश्चिम में नंगा पर्वत से पूर्व में नाम पर्वत तक स्थित है।
- वृहत् हिमालय मध्य हिमालय से मेन सेंट्रल थ्रस्ट के द्वारा अलग होती है।
- विश्व की सर्वोच्च चोटी माउण्ट एवरेस्ट इसी हिमालय पर अवस्थित है।
- इसकी औसत ऊँचाई 1800 से 3000 मी. है।
- पीरपंजाल श्रेणी इसका पश्चिमी विस्तार है।
- इस श्रेणी के दक्षिण-पूर्व की ओर धौलधा, नाग, रीवा मसूरी आदि श्रेणियां पायी जाती है।
- इन श्रेणियों पर शिमला, मसूरी, नैनीताल, रानीखेत, अल्मोड़ा, दार्जिलिंग एवं डलहौजी नगर स्थित है।
- मध्य और महान हिमालय के बीच पश्चिम में कश्मीर की घाटी तथा पूर्व में काठमाण्डु घाटी है।
- यहाँ पर कोणधारी वन मिलते हैं तथा ढालों पर छोटे-छोटे घास के मैदान पाये जाते हैं जिन्हें कश्मीर में मर्ग (गुलमर्ग, सोनमर्ग) - और उत्तराखंड में वग्याल और पयार कहते हैं।
- इसकी औसत ऊँचाई 900 से 1200 मी. के बीच है
- शिवालिक एवं मध्य हिमालय के बीच अनेक घाटियाँ पायी जाती है।
- इसको पश्चिम एवं मध्य भाग दून / देहरादून और पूर्व में द्वार जैसे हरिद्वार कहते है।
- हिमालय की दो घुमाव युक्त एव मोड़दार भुजाएं हैं।
- पहली हिन्दुकुश, सलेमान और किरधर श्रीणया के नाम से है।
- इसमें खैबर, बोलन और गोमल आदि दरे हैं ओर उत्तर-पूर्वी में गारो, खासी. जयन्तिया, पटकोई, लुसाई की पहाड़ियां आदि हैं एवं इसी का घुमावदार विस्तार भारत म्यांमार सीमा पर अराकानयोमा पर्वत के नाम से फैला है।
- भारत में 247 द्वीप है जो बंगाल की खाडी (204) तथा अरब सागर (36 द्वीप) में बिखरे हैं।
- अंडमान निकोबार द्वीप समूह बंगाल की खाड़ी में स्थित भारत का सबसे महत्वपूर्ण द्वीप है।
- इनमें नारकोंडम, सुसुप्त एवं बैरन द्वीप सक्रिय ज्वालामुखी है।
- अंडमान द्वीप की सर्वोच्च चोटी सैंडल पीक है।
- भारत का दक्षिणतम बिन्दु पिगमेलियन प्वाइन्ट (इंदिरा प्वाइंट) ग्रेट निकोबार पर स्थित है।
- पम्बन द्वीप मन्नार की खाड़ी में स्थित है।
- हरिकोटा द्वीप आन्ध्रप्रदेश में स्थित है।
- लक्षद्वीप अरब सागर में स्थित प्रवाल भित्ति द्वीप है।
- अमीन दीव लक्षद्वीप का सबसे बड़ा द्वीप है।
- कावारत्ती लक्षद्वीप की राजधानी है।
- कराकोरम जम्मू-कश्मीर राज्य में स्थित है इसकी 60 से अधिक चोटियां 7000 मीटर ऊँची हैं।
- यह श्रृंखला 500 किमी. लंबी है और ध्रुवों के बाद सबसे अधिक हिमाच्छादित है।
- सियाचिन और बियाफो ग्लेशियर इसी क्षेत्र में अवस्थित हैं। सियाचिन दुनिया की दूसरी बड़ी ग्लेशियर है। गिलगिट, सिंधु एवं श्योक नदियाँ कराकोरम की दक्षिणी सीमा निर्धारित करती हैं
पटकाई बुम या पूर्वांचल म्यांमार से लगती भारत की पूर्वी सीमा पर स्थित है।
2. वृहत् मैदान :
- सिंधु-गंगा का मैदान, जिसे वृहत् मैदान के नाम से भी जाना जाता है, सिंधु और गंगा-ब्रह्मपुत्र नदी श्रृंखला का सबसे बड़ा मैदान है।
- यह हिमालय पर्वत के समानांतर जम्मू-कश्मीर से लेकर असम तक फैला हुआ है।
- यह 7,00,000 वर्ग किमी. क्षेत्र में फैला हुआ है।
- गंगा और सिंधु इस क्षेत्र की प्रमुख नदियां हैं।
- व्यास, यमुना, गोमती, रावी, चिनाब, सतलज एवं चम्बल इसकी सहायक नदियां हैं।
- भाबर क्षेत्र
- तराई क्षेत्र,
- बांगर क्षेत्र
- खादर क्षेत्र।
ये मैदान दुनिया के सबसे सघन खेती वाले क्षेत्र हैं। चावल और गेहूँ इस क्षेत्र की मुख्य फसल है। यह मैदान सघन आबादी का क्षेत्र है।
3. प्रायद्वीपीय उच्च भूमि :
छोटानागपुर का पठार कई धातु अयस्क कोयले का भंडार है।